Deep Dive into `istioctl create-remote-secret`
Istio’s multicluster mode enables a service mesh to span across multiple Kubernetes clusters. One crucial utility to make this work is istioctl create-remote-secret. This post is a deep dive into what this command does, how it works under the hood, and how to troubleshoot common issues.
What does create-remote-secret do?
The command generates a Kubernetes Secret that contains credentials allowing a client cluster (usually the Istiod control plane) to access a remote cluster’s API server.
Example Usage
1
2
3
4
5
istioctl create-remote-secret \
--name=cluster-1 \
--kubeconfig=/home/vikas/.kube/cluster-1 \
--server=https://172.18.0.6:6443 \
| kubectl --kubeconfig=/home/vikas/.kube/cluster-0 apply -f -
You can also use a context name instead of a kubeconfig path. The --server flag specifies the remote cluster’s API endpoint that must be reachable from the client cluster.
What Happens Internally
The istioctl create-remote-secret process involves several steps that happen across both clusters. Let’s break down each step:
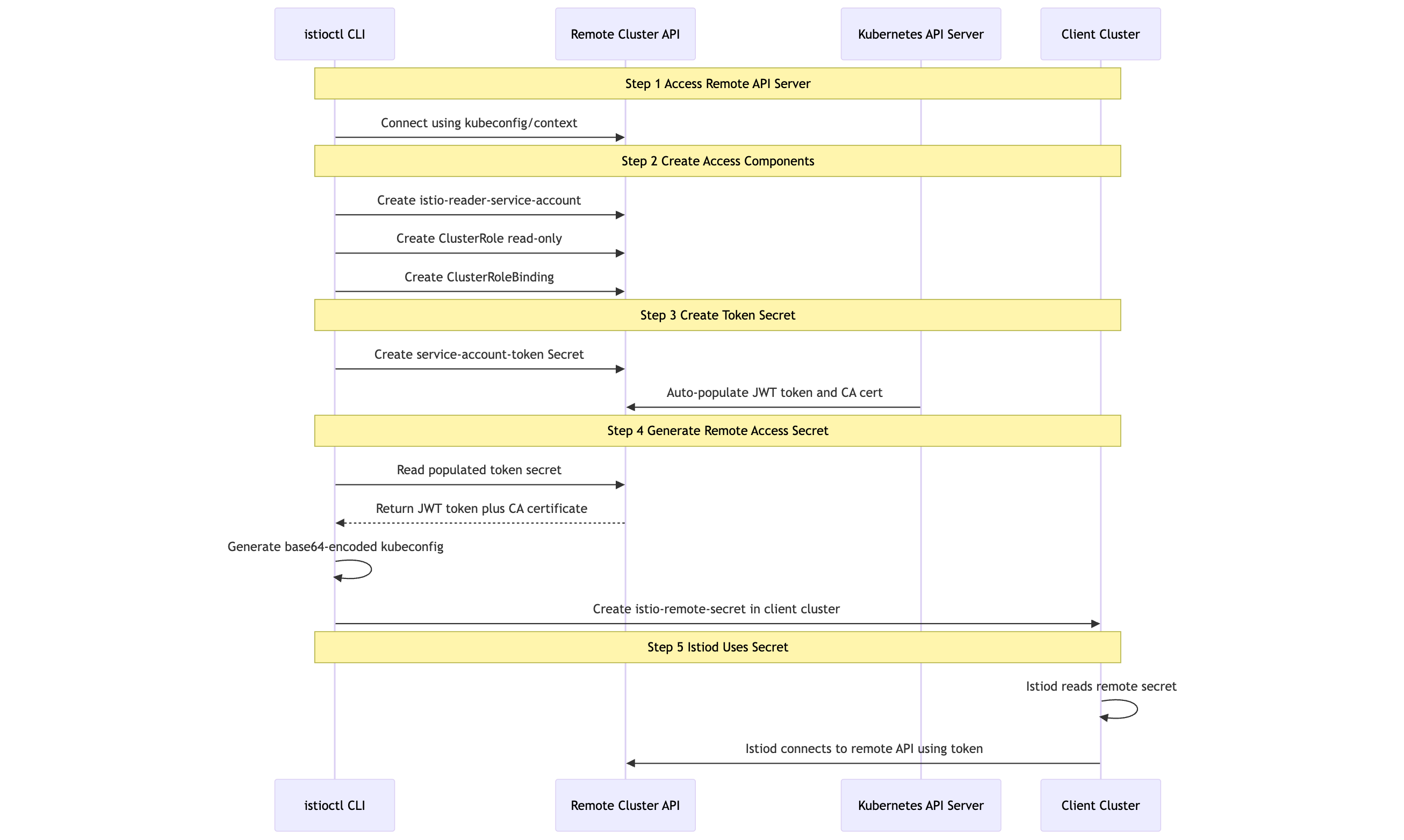 Complete flow of the create-remote-secret process
Complete flow of the create-remote-secret process
Step 1: Accessing the Remote API Server
istioctl uses the Go Kubernetes client to talk to the remote API server, either via the given --kubeconfig or --context.
Step 2: Creating Access Components
It ensures the following are present in the remote cluster:
- A ServiceAccount named
istio-reader-service-account - A ClusterRole with read-only access
- A ClusterRoleBinding to associate the role with the service account
Step 3: Creating a Token Secret
Next, it creates a Kubernetes secret of type kubernetes.io/service-account-token. This is a special secret—the API server fills in a JWT token automatically.
1
2
3
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: istio-reader-service-account
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
This secret will contain:
token: The JWT tokenca.crt: The cluster CA certificatenamespace: Namespace of the service account
Step 4: Generating a Remote Access Secret
Once the JWT token is filled, istioctl generates a new Opaque secret containing:
- A base64-encoded kubeconfig (with the service account JWT)
- Cluster metadata
This secret is applied to the client cluster, allowing the local Istiod to reach and discover resources in the remote cluster.
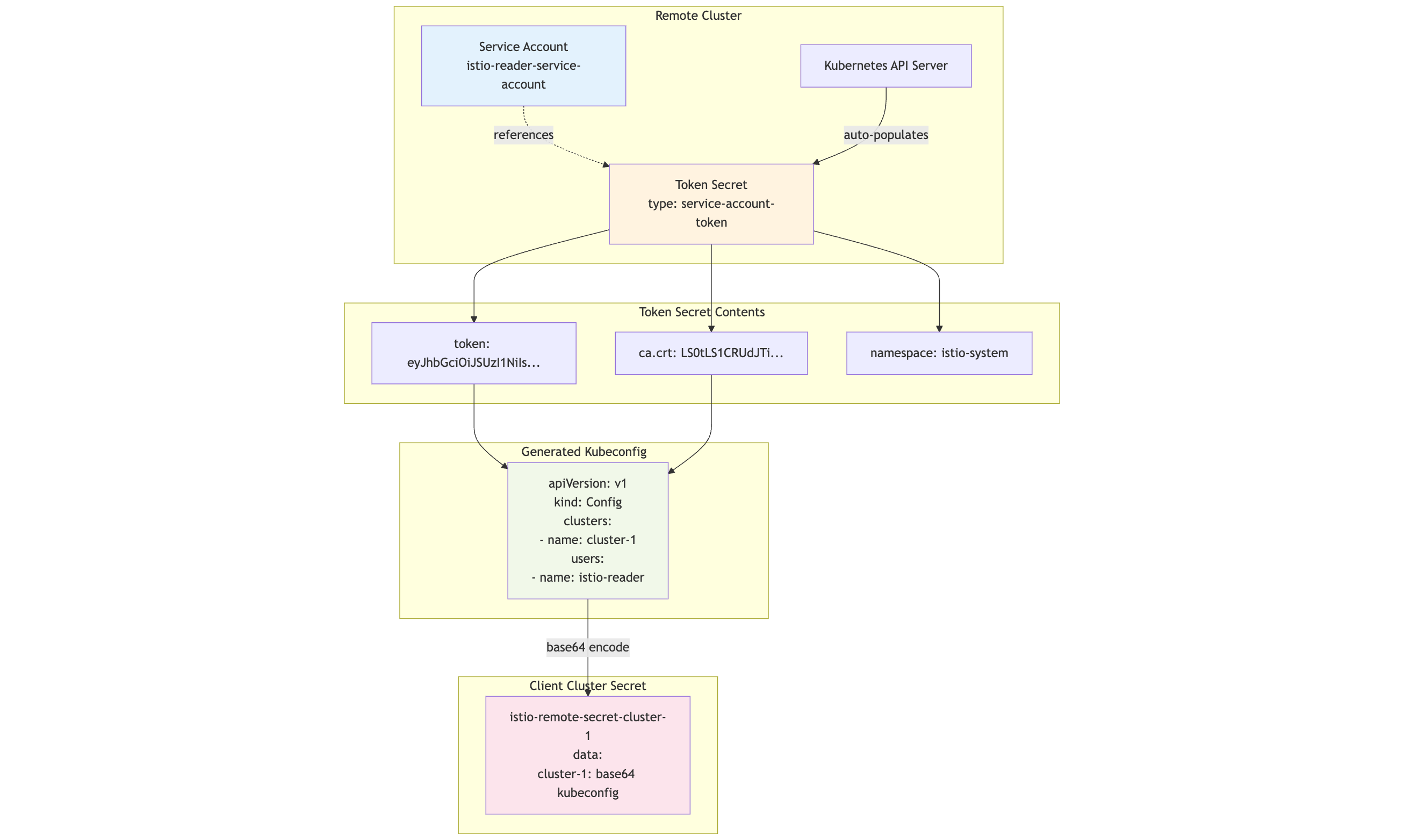 Detailed view of how the service account token is generated and packaged
Detailed view of how the service account token is generated and packaged
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: istio-remote-secret-cluster-1
namespace: istio-system
labels:
istio/multiCluster: "true"
istio.io/cluster: cluster-1
type: Opaque
data:
cluster-1: <base64-encoded kubeconfig>
You can decode the kubeconfig using:
1
2
kubectl get secret istio-remote-secret-cluster-1 -n istio-system \
-o jsonpath='{.data.cluster-1}' | base64 -d
Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common issues and how to resolve them:
Server URL Format Make sure --server starts with https://, not just IP:port.
Test Kubeconfig Manually First, decode the base64-encoded kubeconfig from the remote secret to see the actual kubeconfig and JWT token:
1
2
kubectl get secret istio-remote-secret-cluster-1 -n istio-system \
-o jsonpath='{.data.cluster-1}' | base64 -d > /tmp/remote-kubeconfig.yaml
Then copy the kubeconfig from there and test it:
1
KUBECONFIG=/tmp/remote-kubeconfig.yaml kubectl get pods -A
Test Raw Token Access
1
curl -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" https://172.18.0.6:6443/version
Check RBAC in Remote Cluster Verify the following resources exist:
- ClusterRole
- ClusterRoleBinding
istio-reader-service-account
Summary
The istioctl create-remote-secret command bootstraps remote access credentials from one Kubernetes cluster to another, enabling Istiod to operate across clusters in a multicluster Istio mesh.
By understanding each step of the process—service account setup, token generation, kubeconfig construction—you can confidently debug and validate multicluster connectivity.
Pro Tip: Always test the generated credentials manually before deploying to production to ensure proper connectivity between your clusters.
Warning: The generated service account tokens have cluster-wide read access. Store and handle these secrets securely.